By JY Mon Jan 1 14:26:52 2018
Again here comes 2018, like in the past I try to write a short summary to
remind myself what happen in the previous year.....
2017 started somewhat disappointing but didn't do too bad at the end, yet
still, its the first time in 5 years our net cash flow dipped below 500k, I
continue to pay down additional principles to the banks, bringing debt to
asset ratio close to 33%, goal is under 30% before next recession.
And thanks to a stronger than expected appreciations with the local real
estate market, our personal real estate portfolio exceed 11 million the
first time.
--------
Realized Net Cash Flow ( Combine all sources, including regular principal
payments ) - $494,000.
Unrealized Appreciations ( including a one-time appraisal adjustment) - $873
,000
----
This is my personal portfolio, the group portfolio is about 25+ million strong.
----
Personally I hold 173 units.
Road to Financial Freedom
Tuesday, August 21, 2018
Wednesday, January 17, 2018
Mice problem? Should I Hire a Mice Exterminator or Get Rid of Mice Myself?
Should I Hire a Mice Exterminator or Get Rid of Mice Myself?

This stone foundations is vulnerable to mice infestation. All stones must be perfectly repointed outside and in.
Before trying to get rid of mice on your own, consider what a mice exterminator can do.
A mouse in the house can create a mix of fear, disgust, and filth, and left unchecked, will quickly turn into dozens or hundreds of mice. It is possible to get rid of mice yourself as a DIY owner/manager, but there are definite advantages to hiring a mice exterminator as well. This article reviews the basics.
Know Thy Enemy
According to Wikipedia, mice are — along with humans — one of the most successful groups of mammals on the planet. They are remarkably adaptable to varying food sources and environments. They reproduce quickly and in large numbers.
In the wild, mice eat fruits and grains from plants. In manmade settings, they will eat anything, including pet food, chocolate, peanut butter, and meat scraps.
On a per-weight basis, mice eat ten times more food than people. NPR reported that the average American eats close to 2,000 pounds a year, and the CDC reported an average body weight (men and women) of 182 pounds, which equates to eating 1.5% of our body weight each day. A mouse eats 15% of its bodyweight each day.
Mice are fertile when they’re about 50 days old. Gestation of a new litter takes 20 days, and under optimal conditions, produces 10 to 12 pups. Weaning takes three weeks, and then two to five days later the female can conceive again.
Well cared-for pet mice can live for approximately two years (the record is four years, see the rodent link below). This means a single breeding pair could theoretically produce approximately 150 offspring. This figure is highly dependent on temperature and food availability.
Mice teeth (like the teeth of other rodents) have evolved to grow continuously so they can continually be filed down and sharpened. This is partly why mice can destroy moldings, casings, walls, and electrical wiring.
Get Rid of Mice Yourself
Mice are inside to look for nesting material in the early fall and food sources throughout the winter. As an owner, there are many things you can do to get rid of mice yourself.
First, eliminate access to loose fluff, fiberglass insulation, blow-in insulation, old carpet, and other nesting materials.
Second, close off interior chaseways like holes for electrical wires and pipes. If you have forced hot water heating, pay special attention to the holes around those pipes. They should be blocked with a copper wool mesh and black PUR foam. If you seal up all the chaseways in all your units, it will take an hour or two per unit. You will want knee pads, a flashlight, a butter knife or dowel, more copper wool than you think you need, tin snips, a trash bag, and PUR foam gun with a can or two of foam.
To close a chaseway, use the tin snips to cut off an appropriately sized piece of copper wool. Do this over your open trash bag to catch metal shards. Shape the copper into a donut, place it around the pipe and against the hole, and use the butter knife to jab the copper wool firmly into place. Squirt black foam around it. Don’t use “great stuff,” which is easier to chew through, and don’t do this when the heat is actively working , which can cause the foam to run. Repeat for every hole, no matter how small.
Third, close off exterior access. Pay attention to the lower corners of exterior doors, stone foundations riddled with holes, and the sills between the foundation and the frame. These must all be sealed perfectly to prevent rodent access.
Fourth, seal the interior foundation. Mice can burrow, so sealing the foundation above ground-level is not adequate. Seal the wall from inside the basement down to the basement floor. If you have a dirt floor, it is hopeless; put in a slab.
Fifth, once the place is sealed up, place traps and check them regularly. A mouse that is alive in a trap should be killed immediately for humane reasons. Place your thumb and index finger behind its skull. With your other hand, grab its tail and draw sharply back, holding the head in place. You will feel the spine snap and the mouse will be put to rest.

These forced hot water pipes are inadequately sealed against mice. They need copper wool, more of it than the steel wool pictured, and an application of PUR foam.
Hire a Mice Exterminator
Exterminators are licensed and trained to use lethal rodenticides in a safe way. For instance, under 333 CMR 13.08(1), rodenticides must be placed in tamper-resistant bait stations and secured so as not to be lifted. The bait station must also be labeled to identify the person or company who placed it there, the date it was placed, the EPA registration of the product inside, and the active ingredients of the product.
Applicators are also required to keep logs of where they applied baits, and share those logs with any person upon reasonable request.
As an owner/manager in a litigious age, hiring a licensed exterminator solves several problems beyond mice.
First, there is no question in a court’s eyes that you have taken appropriate action to address a vermin infestation. If it takes a long time to get rid of all the vermin, you won’t have liability the way you might if you were doing it yourself.
Second, you cannot be liable for improper or unlicensed application of a pesticide or rodenticide.
Finally, there’s a good chance that the mice exterminator knows more about mice than what can be learned in a newsletter article.
Whether you decide to hire a mice exterminator or get rid of mice on your own, don’t wait. Mice are one problem that multiply.
A “How To” for Better Tenant Screening
From:
http://masslandlords.net/a-how-to-for-better-tenant-screening/




http://masslandlords.net/a-how-to-for-better-tenant-screening/
A “How To” for Better Tenant Screening
We recently tracked the process of renting out two vacancies in a Worcester three-decker. The results show that this one landlord, at least, could do their tenant screening better. Below we share the statistics on their rental process in the hope that the case study will shed some light on your own business.
Case Study Overview
The Worcester three-decker is owner-occupied. One apartment was almost completely modern and the other was somewhat antiquated. Both had been priced barely below market and within the payment standards for Section 8.
The landlord has a history of compliance with all fair housing laws. For this owner-occupied property, the landlord was concerned that tenants would follow house rules, especially quiet hours and a no-smoking policy for the entire property (even outside). The landlord had an additional preference not to accept dogs on account of possible noise and yard filth. These concerns stacked on top of the basic concern that tenants would be able to pay. First and security were required to move-in. Tenants were evaluated using our applicant qualifier.
The first vacancy began on March 1 and was filled on March 26th for an April 1 start. The second vacancy began on April 1 and was filled on April 29 for a June 1 start. Three months of vacancy between two units was longer than the landlord wanted.
The only advertisement for the vacancies was done with craigslist posts, following our advice. The ad clearly directed tenants to call a cell phone, and the landlord took the calls more or less as they arrived. If the call was not picked up the call went to voicemail. Prospective tenants could also email.
The landlord’s process required an initial phone screen. Whether tenants emailed or called, the landlord used our phone screening prompt sheet to find out basic information.
A prospective tenant who passed the phone screen was scheduled for a one-on-one tour of the apartment. All prospective tenants who attended a tour were given our rental application.
Tenants who completed a rental application were scored on our applicant qualifier. Low-scoring tenants were notified of the deficiency and had at least one opportunity to correct it by providing additional information.
Tenant Run-Down
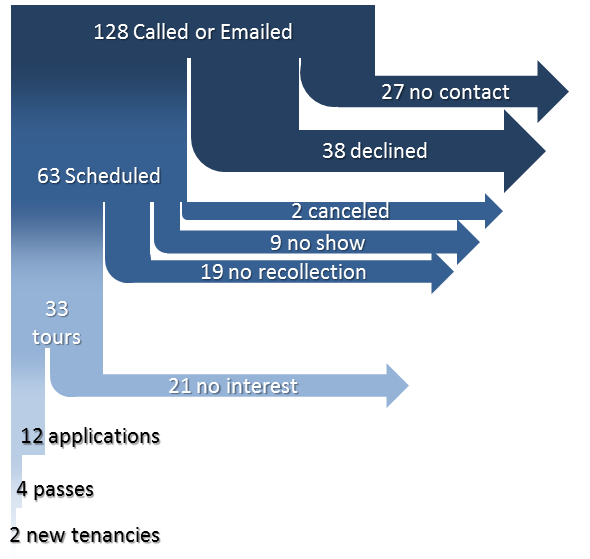
The figure below shows this landlord’s data.

Flowchart of the tenant screening process for a Worcester, MA case study.
128 households called or emailed the landlord inquiring about the apartment. Here is where the drop-off begins:
- Households that left a voicemail or email but could not afterwards be reached: 27
- Households that were declined by the landlord during the phone screen: 38
- Vaping: 1
- Smoking: 17
- Income grossly less than 3x prospective rent: 11
- Not a first time renter, but unable to provide either good credit or any kind of landlord reference: 2
- Stated desire to operate a high traffic business out of the unit: 1
- No expectation of getting required move-in money: 3
- Dogs without doctor’s notes: 3
- Households that were scheduled for a tour: 63
- Drove by beforehand and canceled the tour: 1
- Incorrectly thought heat was included, reread the ad, and canceled the tour: 1
- Did not cancel but did not show up: 9
- Definitely attended the tour (landlord made a note or remembers): 33
- Probably didn’t show (landlord failed to note but has no recollection of meeting that tenant): 19
- Households that applied: 12
- Received a passing score: 4
- Preferred a different apartment: 1
- Given the chance to provide move-in monies: 2
- Lower scoring and not given the chance: 1
- Households that failed to complete all required documentation before another: 6
- Households that gave up part-way through: 2
- Received a passing score: 4
- Households that applied: 12
Observations
Renting an apartment is a significant time sink. (This is why realtors often claim one month’s rent as their fee.)
As this landlord found out, it’s very important to answer the phone when it rings and to reply to emails promptly. Approximately 20% of first contacts went flat, meaning that the tenant was initially interested in the apartment, reached out, and then found a more promising apartment before the landlord returned their call. The number one biggest cause of early rejection would seem to be the tenants rejecting the landlord for being unavailable or not returning calls quickly enough.
Another significant time sink was the number of tenants who were not prepared to rent this apartment. The two biggest causes of rejection at the phone screen stage were ignoring the “no smoking” part of the ad (13% of callers) or being unprepared to take on the financial responsibility (11% of callers). The landlord rejected nearly a quarter of all applicants over the phone.
Thoughts on Smoking
The landlord’s ad said, “This is a no-smoking property.” All smokers who called about the apartment admitted that they smoked but offered not to smoke inside the apartment. The landlord wanted no smoking anywhere at all (not on the porch, in the lawn, or anywhere near any windows). The landlord also believed that in the winter, when temperatures dropped, smokers were likely to break their promise not to smoke inside. This didn’t make the landlord any new friends, but all smokers were told they were better off renting elsewhere.
Thoughts on Section 8
This landlord observed that tenants receiving public assistance made this fact known during the phone screen. Tenants routinely asked “Do you accept Section 8?” Presumably there are some other landlords who say no, otherwise why would a tenant ask? The law prohibits the landlord from refusing to take Section 8. A landlord cannot discriminate on the basis of receiving public assistance.
Did this landlord turn away any Section 8 tenants? Absolutely. Almost all of the tenants unable to meet the financial requirements had Section 8. Section 8 does not pay for security deposits, and it does not require a landlord to relax their application standards. So tenants without a security deposit or without adequate income could not qualify for the apartment.
(Note: This landlord used the correct way to calculate a Section 8 tenant’s income ratio. Divide the applicant’s income by their share of the rent. Section 8 screening is actually very complicated and will be discussed in another article.)
Recommendations
1. Try open houses as a way to meet more tenants in less time.
This landlord gave somewhere between 21 and 40 tours (they don’t have accurate notes on no-shows). This one-on-one probably was more costly than it needed to be. If they had instead scheduled open houses (aka, group tours), they would have reduced the impact of no-shows and the total time spent showing the apartment.
2. Respond to calls and emails on the same day, before a tenant forgets your apartment ever existed.
As noted above, almost a quarter of this landlord’s leads went cold in the very first contact.
3. Continue using phone screens as a way to gain information early and save time.
The chart above shows that roughly a quarter of callers could be screened away for obvious non-starters. This saved time for all concerned.
4. Do not bother showing an apartment unless it is rent-ready.
Although we didn’t discuss it above, this landlord had not finished painting when the second apartment was first being shown. This likely left all the earliest, most proactive tenants with a feeling that the apartment was not ready or not good enough. This renovation work combined with the landlord’s difficult behavioral criteria likely contributed to the extra month’s vacancy experienced (the June 1st start date).
5. Continue to engage in dialog over application completeness and objective point scoring.
One thing the landlord did very well was to engage in dialog about the application process. Although only 4 applications received passing scores, none of them passed on first glance. All 12 applications required additional supporting materials, like pay stubs, bank statements, or doctor’s notes. All applicants were given the chance to provide this information. This dialog sharply reduced the chance that the landlord would be found non-compliant with fair housing laws. Most importantly, it turned some dud applications into passing scores.
Conversion Analysis
The ideal situation would have been this: one tenant called, passed the phone screen, loved the apartment, applied, got approved, and gave the landlord their move-in money. One call, 100% conversion. Easy!
In reality, the actual conversion rates at each step were far less.
Examining Step One: Phone Screening

Conversion rates for phone screening.
As stated above, the 21% of “no contact” were missed calls that the landlord should have been on top of. Of the remaining, roughly five tours were scheduled for every three households rejected. Another way of saying the same thing: five tours were scheduled for every eight calls. This means that if the landlord had not missed those 26 calls, they would have had another (5 divided by 8) times (26) = 16 tours. This would have increased their schedule rate from 49% to 61%.

If the landlord had not missed as many calls…
Landlords with offices sometimes do not do any phone screens whatsoever. They require the prospective tenant to show up and complete a questionnaire. This is fine as long as the questionnaire encourages honest answers. This landlord did not have an office.
Phone screens and questionnaires can be really distracting. The landlord found phone screens difficult, especially when the craigslist ad was refreshed and a wave of new calls began. But they were far less wasteful than giving a tour and processing a full rental application for all 128 callers. Every time this landlord excluded a prospective tenant up-front, it saved both them and the prospective tenant valuable time.
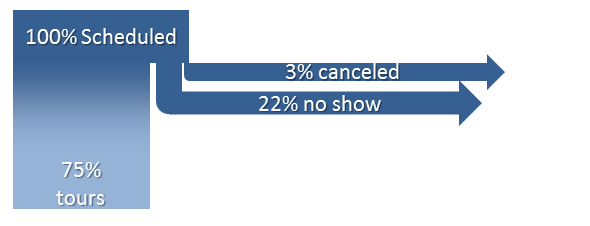
Examining Step Two: Tours
The landlord scheduled 63 tours. Consider these tenants the new “100%”. The landlord didn’t keep records for 30% of them. They might have taken a tour, they might not.

Drop-offs at the “tour” part of the process.
It looks like there were roughly three times as many tours as there were no-shows and cancellations. Said another way, three out of every four tours actually took place. We’ve redrawn this step in the process to attempt to correct for the lack of data. We think probably 75% of the “no recollection” candidates actually did take tours, or 14 households, and the remaining 5 probably failed to show.

The percent of tours actually given is probably more like this.
This landlord owner-occupied the building, so a no-show was not a big deal for them. But for any other landlord or for a realtor, no-shows would have been a huge waste of time. All the time spent driving there and back would be utterly wasted. Some of the 63 tours might have been combined into “open house” events as a time saving measure. It probably would not have increased the number of tenants who applied for the apartment. (If we get data on it, we will post it.)
Examining Step Three: Applications
If it’s true that 75% of scheduled tours did take place, then there would have been 47 tours. But since this doesn’t change the number of applications received (12), we now find another problem. Almost three-quarters of all tours did not result in an application.

The percent of tours that apply may be too low.
This ratio may compare with what you find in your own business. Every apartment is unique and not all apartments are appealing to all households. But the advice for this landlord is clear: make sure the apartments appear to be good value.
The image of apartment #2’s kitchen (at the top of this article) shows old cabinets and a small sink. We also know that apartment #2 was still being painted. It’s possible that the landlord could have increased this application ratio if this unit had been rent-ready during tours.
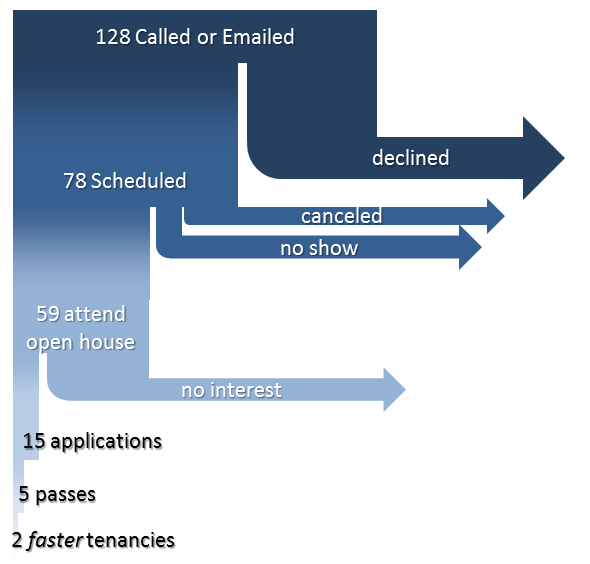
What If
If our recommendations had been made at the outset, the landlord would have had more invitees to open houses (61% instead of 53%). And with a rent-ready apartment, they would have had more applications (we’ve estimated 15 instead of 12). They would have had this for the same amount of work. All they did was change the process a little.
This would have given the landlord at least another three applications, and very likely one of them would have been qualified. Maybe that one would have taken the apartment for May 1 instead of June 1. We can’t say for sure. But more applications for no additional cost sounds worthwhile to us.
The revised process with increased numbers:

So those are our recommendations for better tenant screening. Overall, this landlord used a rigorous process and made good use of our forms.
Was this insightful? Let us know in the comments below!
Thursday, November 30, 2017
Schedule E: Repairs vs. Supplies
The difference between Supply and Maintenance Expenses for rental properties
Repairs – include all repairs made to the property that were not considered capital improvements. Expenses here will be small repairs and not the replacement of floors, roofing, etc. You may also include De Minimis Safe Harbor expenses here if they are less than $2,500 and you make the annual election.
Supplies – include the cost of incidental materials and supplies such as paper for printing, small tools, and other small miscellaneous materials that don’t fit into another category.
Questions:
Are expenses such as painting supplies, blinds, lights and cabinetry hardware considered supply expenses or maintenance expenses for rental properties
More answers:
Supplies are usually consumable items. Light bulbs you purchased for the rental unit and any cleaning supplies you purchased specifically to clean the rental unit are examples of a Schedule E "Suppllies" expense. In practice, the IRS does not really care whether you claim these things as supplies on your Schedule E or just lump them into your maintenance/cleaning expense on Schedule E.
Repairs – include all repairs made to the property that were not considered capital improvements. Expenses here will be small repairs and not the replacement of floors, roofing, etc. You may also include De Minimis Safe Harbor expenses here if they are less than $2,500 and you make the annual election.
Supplies – include the cost of incidental materials and supplies such as paper for printing, small tools, and other small miscellaneous materials that don’t fit into another category.
Questions:
Are expenses such as painting supplies, blinds, lights and cabinetry hardware considered supply expenses or maintenance expenses for rental properties
Recommended Answer
29 people found this helpful
The items you listed would be considered Maintenance Expenses.
Supplies would be more like cleaning products or rakes. Supplies
would be something that you use but don't leave at the house.
More answers:
Supplies are usually consumable items. Light bulbs you purchased for the rental unit and any cleaning supplies you purchased specifically to clean the rental unit are examples of a Schedule E "Suppllies" expense. In practice, the IRS does not really care whether you claim these things as supplies on your Schedule E or just lump them into your maintenance/cleaning expense on Schedule E.
The Ultimate Guide to IRS Schedule E for Real Estate Investors
https://www.therealestatecpa.com/2016/05/22/ultimate-guide-irs-schedule-e/
Whether you’re a brand new investor trying to do it yourself or you have a million dollar portfolio and have a team of professionals, it’s always a good idea to have foundational knowledge of each aspect of your business. I developed this comprehensive guide to allow real estate investors on every level better understand IRS Schedule E.
While real estate tax can be complex, this guide is written for investors of all skill levels. I could have made it cumbersome and technical, but then my audience would be other CPAs which isn’t the intent of this article, much less The Real Estate CPA™ as a whole.
Let’s begin by highlighting all the great knowledge you’ll walk away with after you get through this article:
Think of earned income as business income. Earned income is generated from an active trade or business. You pay self-employment tax on earned income. Real estate, royalties, partnerships, and S-Corporations can all generate earned income.
For example, you may run a real estate business where you are flipping or developing properties where you’d be required to report your income on IRS Schedule C; the schedule in which you report earned income.
Or you may be an owner in a partnership or S-Corporation and have a combination of earned income and supplemental income. In this case, one business can be reported on both IRS Schedule C and E.
IRS Schedule E is used for supplemental income which is generally considered passive income. As an investor, this is important because rental real estate generates passive income and, as such, we will report the income and loss from rental real estate on Schedule E.

The first and most important place you will see the end result of IRS Schedule E appear is line 17 of your IRS Form 1040. Here you should see the full amount of net income or loss from your rental properties.
If your activities on IRS Schedule E created a loss and your loss is not showing up on line 17 of IRS Form 1040, you may be limited by the Passive Activity Loss limitations. While the Passive Activity Loss limitations demand an entirely separate post on their own, here’s a high level overview:
Many investors get worried when they hear this. They’ve been told real estate is a beautiful way to shelter income from taxes but now they are being barred from taking the well deserved losses.
What happens to the losses if you cannot claim them? They are called “unallowed losses” and are reported on IRS Form 8582. This form serves as a catchall that will keep track of all the losses you have not been able to claim over the years.
You do not “lose” these losses; they are simply carried forward until they can offset net rental income. These losses can also be used to offset the gain if you were to sell a rental property, regardless of whether or not the rental property you are selling generated the specific loss.
If the losses get carried forward and you can’t use them, doesn’t that defeat the purpose of sheltering income from taxes?
This is where I have to tell you that you’ve been gurued. Real estate is indeed an excellent way to legally avoid taxation, but for high income earners, you will only be avoiding tax on the rental income, not your regular income from your job.
Again, some amount of income or loss from your rentals should appear on line 17 of your IRS Form 1040. If your adjusted gross income is over $150,000, then you should look for IRS Form 8582 and see if the rental loss has been carried over to it.
The most common advice is that the rental property basis is the purchase price plus improvements. So if you buy a property for $100,000 and add $10,000 in improvements, the property basis is $110,000.
This advice, while correct, can be misleading. If you are unaware that you must allocate a portion of the purchase price to land, you will calculate the wrong depreciable basis and therefore deduct an incorrect amount of depreciation.
It’s important to understand how to determine the value of the land of a purchased property. In most cases, the easiest way to get this value is to pull the property’s tax card from the county assessor’s office. Doing so will provide us with a “land ratio” which we will then apply to the purchase price.
For instance, if the property tax card says that the land is worth $10,000 and the improvements are worth $40,000, then our land ratio is 20% [$10,000/($10,000 + $40,000)]. We would then apply this ratio to the purchase price of the property to determine how much value we allocate to land and how much we allocate to improvements.
Why is this important? Because we can only depreciate the value of improvements since land is non-depreciable. Land is ever lasting and does not deteriorate.
 A too common mistake I see is depreciating the entire purchase price
of the property. This is not correct accounting and will need to be
corrected via alternative methods. Don’t make this mistake!
A too common mistake I see is depreciating the entire purchase price
of the property. This is not correct accounting and will need to be
corrected via alternative methods. Don’t make this mistake!
Okay, now that we know we can’t depreciate the land value of the building, let’s figure out how to calculate the property basis.
The first thing that I do when preparing IRS Schedule E is a closing cost analysis. I have developed a calculator that helps me quickly calculate a property’s basis.
Resource: Property Basis and Depreciation Calculator
The Closing Cost and Depreciation Calculator is an excellent tool to use when calculating a rental property’s basis because it analyzes all sorts of closing costs such as title transfer fees, bank fees, loan origination fees, escrow, and seller credits. It then places them into the appropriate buckets which we’ll discuss below, and calculates depreciation and amortization for the first year and on an annual basis.
I recommend using some sort of tool, calculator, or guide to help you with the analysis of your closing costs and depreciation because you are going to be lumping costs into three distinct categories:
From the property basis, we’ll subtract out our land value to determine the total value in which we will begin depreciating. This is called the depreciable basis.
Purchase Price + Closing Costs – Land Value = Depreciable Basis
Depreciation will usually be over a period of 27.5 years. If you are investing in commercial property, you’re looking at a 39 year period.
Related: How to Calculate Rental Property Depreciation Expense
There are several depreciation methods and conventions. We will be using the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) for our depreciation purposes.
While it sounds like a mouthful, all you need to know is that when you first place a property into service (i.e. advertise it for rent), you will be granted a half month of depreciation. Then, during the first year, you’ll calculate depreciation on a monthly basis.
So if I buy a property and advertise it for rent on September 29, for the first year I’ll have 3.5 months of depreciation (1/2 September + October + November + December). If my annual depreciation is $1,200, I first divide that value by 12 to get it on a monthly basis, then multiply it by 3.5 to figure my first year of depreciation. In our example, it will be $350.
The second category is the loan cost basis which is the sum of all costs associated with the loan. These can be the origination fee, credit report, bank fees, and appraisal fees if one was required by the lender.
Once we calculate the loan cost basis, we will need to determine our annual amortization. Amortization essentially means the same thing as depreciation, it’s just the depreciation method for “intangible” costs.
You will amortize your loan costs over the life of the loan. So if you have a 15 year loan, your amortization period is 15 years. If you have a 30 year loan, your amortization period is 30 years.
Let’s assume our loan cost basis is calculated to be $3,000 and we have a 30 year loan. Each year, you will write-off amortization expense of $100 ($3,000/30 years).
The first year of amortization is calculated much like depreciation in that you will be granted a half month for the month you place the property into service and then amortize on a monthly basis until the end of the year.
The third category is currently deductible expenses which consist of hazard insurance, property taxes (not transfer taxes), and other miscellaneous expenses. These expenses do not need to be amortized or depreciated (whew!) but are simply deducted in full the first year.
For the do it yourself investors, this section will be your tax preparation bible. For all of my clients and everyone who already has a CPA, use this section to cross check the CPA’s work.
The first section is seemingly the easiest but trips plenty of folks up. First, we have to determine whether or not we made any payments that required a 1099. As a general rule, you must issue a 1099 to contractors whom you’ve paid over $600 for work during the year. But luckily for most of my readers, landlords are excluded from this rule.
So if you are a landlord, the common practice is to tick the “no” box when asked if you made payments that require a 1099.
Next we’ll enter the property address and the type of property (single family, multifamily, etc). Hopefully this doesn’t require much more explanation.
Now we need to determine fair rental days, personal use days, and whether or not we are operating a qualified joint venture.
For fair rental days, put the number of days the property was actually rented and producing income. This is especially important if you have rented the property for 14 days or less as then your rental income won’t need to be reported.
Personal use days must also be inputted and can sometimes be confusing. You will only input personal use days if you have used the entire building for personal purposes, or anyone in your family has used the entire building for personal purposes.
So, if you are house hacking (living in one unit and renting out the others), you will not report any personal use days. Instead, you will just split common expenses (mortgage, insurance, property taxes) between IRS Schedule A and E.

When rental property is jointly owned by spouses who are not located in a community property state, we have a problem. The spouses must either report their income and losses on a partnership tax return (complicated!) or elect the qualified joint venture status.
Per the IRS Schedule E instructions: “If you and your spouse each materially participate as the only members of a jointly owned and operated rental real estate business and you file a joint return for the tax year, you can elect to be treated as a qualified joint venture instead of a partnership.”
When you and your spouse jointly own an entity that owns your rental property, it can get complicated fast. That discussion is beyond the scope of this post, but you will need to speak with a CPA to sort everything out.
On to the good stuff.
Next we are going to report the rental income received. This is going to be all gross income received from your tenants throughout the year. Gross rental income should include: rental income, refunds received for utilities, and pro-rated rents when you purchased the property.
Expenses are where the tax avoidance (legally) comes into play. I wrote a quick blurb on what to report per expense item:
Advertising – include all general marketing and advertising costs. These can include the cost to place rent signs in the front yard, to advertise on certain websites or publications, to buy business cards, and to send mailers.
Auto and Travel – include all ordinary and necessary auto (to be discussed later) and travel costs required to maintain your rentals. This should not include auto and travel costs incurred to purchase your first rental or to expand your rental business into a new geographic location. Also include 50% travel meals.
Cleaning and Maintenance – include all cleaning expenses to prepare a unit for a tenant or once a tenant moves out. Include maid expenses here as applicable. You should also include maintenance expenses such as painting, mowing, and small upkeep costs of the building, appliances, and equipment.
Commissions – include realtor or property management commissions paid to find a tenant for your unit.
Insurance – include homeowners, hazard, and flood insurance here. Do not pro-rate your annual insurance. You will only report the amount of insurance that you actually pay to your insurance company, not the amount that you pay into escrow.
**A note about escrow – it’s very common to pay insurance and property taxes into escrow on a monthly basis. This protects the lender from your failure to pay these expenses. It’s important to understand that when you pay these expenses into the lender’s escrow account, this is not a deductible expense for you. It is only deductible once the lender actually pays those expenses to the county/city or the insurance agent. That’s when you can deduct the expenses. Why? Paying into escrow is essentially moving money from pocket A to pocket B. It’s still your money and technically an asset on your balance sheet.
Legal and Professional Fees – include expenses related to attorney fees, accounting, and costs of business/financial planning related to your rentals.
Management Fees – include the cost to hire an agent or property manager to manage your rental. This may also include special service calls that the property manager incurs to check on the rental.
Mortgage Interest Paid to Banks – include the amount of interest reported to you by the bank on Form 1098. This amount will be the entire interest the bank has received from you during the year, including the interest you paid during closing.
Other Interest – include the amount of interest paid to third parties, whether they are private investors, private businesses, crowdfunding platforms, or relatives. Also make sure that you have sent these people or parties a Form 1099 showing the interest you have paid them. Without a Form 1099 in this case, you may not be able to substantiate the deduction.
Repairs – include all repairs made to the property that were not considered capital improvements. Expenses here will be small repairs and not the replacement of floors, roofing, etc. You may also include De Minimis Safe Harbor expenses here if they are less than $2,500 and you make the annual election.
Supplies – include the cost of incidental materials and supplies such as paper for printing, small tools, and other small miscellaneous materials that don’t fit into another category.
Taxes – include all tax expenses incurred as a result of owning and operating the rental property. This can include property taxes, school district taxes, and special easements or land taxes. Do not include income taxes.
Utilities – include utility expenses that you have personally incurred, even if the tenant has reimbursed you for them. Do not include utility expenses that the tenant has paid for without you ever having to pay for it. The reason we include utility expenses here even if the tenant has reimbursed you for them is because we are reporting the reimbursement as income at the top of IRS Schedule E and we want to offset that income with the expense you incurred.
Depreciation Expense – include the depreciation expenses that we calculated above with our handy Closing Cost and Depreciation Calculator. Depreciation is an imperative part of IRS Schedule E; don’t mess it up!
Other (list) – include all other expenses incurred while operating the rental but that did not directly fit into any of the categories above. Examples of these expenses may include bank fees, education, HOA fees, subscriptions, cost of books, De Minimis Safe Harbor (if not reported in repairs), meals and entertainment, and gifts to clients or tenants. You will itemize each of your “other” expenses on a separate page.
Once we have all of the expenses inputted into our IRS Schedule E, we add them up and subtract them from our gross rental income. The income or loss for each property will be reported on line 21; if line 21 is a loss, line 22 will show you how much of the loss you can actually deduct.
Line 24 will show you the total net income each property has produced if each property showed net income. If the property instead showed a loss, and you are able to take that loss, you will see the amount on line 25.
Remember, your losses may be limited due to the Passive Activity Loss rules. All of that information will be reported on Form 8582 so definitely review that form if you are showing rental losses.
Line 26 of IRS Schedule E will show the total income or loss that will be reported on line 17 of our Form 1040. But before we calculate line 26, we need to look at Part 2 of IRS Schedule E to report any partnership or S-Corporation income and losses.
Partnerships and S-Corporations will provide you with an IRS Schedule K-1 at the end of the year. That information will be reported on Part 2 of IRS Schedule E.
Basically, we are reporting the name of the partnership, whether it’s a partnership or an S-Corporation, whether it’s foreign owned, and what the employer identification number (EIN) is.
We will then want to report the passive income and non-passive income received from the partnership or S-Corporation. This information will come directly from IRS Schedule K-1 that the partnership or S-Corporation provides you.
Entities must go through the same type of reporting we are doing here with IRS Schedule E. While they use different forms, they are reporting the same information and then providing that information on a summarized form – IRS Schedule K-1.
If you have not received IRS Schedule K-1 but you have an ownership stake in a partnership or an S-Corporation, you have a couple of options. The easiest thing to do is file an extension and wait to file your returns until you actually receive the IRS Schedule K-1. The other option is to go ahead and file your returns, and then file an amended return once you receive IRS Schedule K-1.
Okay, that wraps up IRS Schedule E for the most part. Whatever appears on line 26 will also appear on line 17 of your Form 1040. Make sure that flow is happening correctly to avoid issues.
First thing first, if it isn’t documented, you can’t take the deduction. Document everything!
Related: The Real Estate CPA Podcast, Episode #1 – Documentation: The Key to Tax Savings
Next, the question is what should we be documenting? That’s a great question and it depends on your overall strategy.
Many tax advisors recommend using the “actual expense” method in which you record all of your car expenses incurred throughout the year and deduct the portion allocable to the business use. However, it’s important to have a good idea of payoff vs. effort.
Recording and documenting actual car expenses can take a considerable amount of effort. Sometimes, the additional deduction the actual expense method will grant you over the “standard mileage” method simply isn’t worth your time.
I know, you’re probably shocked that a CPA is recommending leaving money on the table. I’m just trying to be realistic.
CPAs want to save you every penny possible without regard to the time it takes you to put all of this information together. They do this because they can show you how much more you saved by working with them and then they can charge you a higher rate.
But if it takes you an additional 10 hours throughout the year to document an additional $500 in deductible business expenses, your tax savings will be your marginal rate multiplied by that $500. So if you’re in the 25% bracket, you’re additional 10 hours of work has saved you $125.
Congratulations, you’ve paid yourself an hourly wage of $12.50.
Now, a $12.50 hourly wage is better than many people, but you are a real estate investor. You have a business to run. Your hourly wage should be over $100.

Related: Tax Write Offs for Car Business Expenses
So what’s my point?
Spend some time estimating your annual deduction using both the standard mileage rate and the actual expense method. Determine, up front, which method will likely yield higher results.
The standard mileage method is great because is very easy to track and takes no time at all thanks to great smart phone apps like MileIQ.
At the end of the year, you’ll compile all of your car expense documentation and report it on page 2, Part V of IRS Form 4562. The total expense will then flow to IRS Schedule E as an Auto Expense.
We talked about what IRS Schedule E is and how it interacts with the rest of your return. On a high level, we went over what costs go into your rental property cost basis and what you need to do to calculate depreciation (see our Cost Basis and Depreciation Calculator here).
We walked through IRS Schedule E and each expense line item and even talked about car expenses.
If you’re hungry for more or looking for a deeper dive, check out the articles referenced throughout this post. If you want to know more about something, contact us at contact @ therealestatecpa.com and throw in a suggestion for a topic. I’d love to hear from you!
The Ultimate Guide to IRS Schedule E for Real Estate Investors
Whether you do it yourself or hire a CPA, real estate investors need to understand how to report rental property on IRS Schedule E. Our guide will help.Whether you’re a brand new investor trying to do it yourself or you have a million dollar portfolio and have a team of professionals, it’s always a good idea to have foundational knowledge of each aspect of your business. I developed this comprehensive guide to allow real estate investors on every level better understand IRS Schedule E.
While real estate tax can be complex, this guide is written for investors of all skill levels. I could have made it cumbersome and technical, but then my audience would be other CPAs which isn’t the intent of this article, much less The Real Estate CPA™ as a whole.
Let’s begin by highlighting all the great knowledge you’ll walk away with after you get through this article:
- What IRS Schedule E is and how it interacts with your tax return
- Why we report rental property on IRS Schedule E
- Calculating the basis and depreciation of your rental property
- A walk through of IRS Schedule E
- How to report auto expenses
What IRS Schedule E is Used For
IRS Schedule E is the form where you will report “supplemental income and loss” related to rental real estate, royalties, estates, trusts, partnerships, and S-Corporations. Emphasis on the fact that we are reporting “supplemental income and loss” and not “earned income.”Think of earned income as business income. Earned income is generated from an active trade or business. You pay self-employment tax on earned income. Real estate, royalties, partnerships, and S-Corporations can all generate earned income.
For example, you may run a real estate business where you are flipping or developing properties where you’d be required to report your income on IRS Schedule C; the schedule in which you report earned income.
Or you may be an owner in a partnership or S-Corporation and have a combination of earned income and supplemental income. In this case, one business can be reported on both IRS Schedule C and E.
IRS Schedule E is used for supplemental income which is generally considered passive income. As an investor, this is important because rental real estate generates passive income and, as such, we will report the income and loss from rental real estate on Schedule E.

How IRS Schedule E Interacts With the Rest of your Return
When you report income or loss on Schedule E, that income or loss is “re-routed” to different areas within your tax return. Your total taxable income or loss is reported on line 26 of Schedule E.The first and most important place you will see the end result of IRS Schedule E appear is line 17 of your IRS Form 1040. Here you should see the full amount of net income or loss from your rental properties.
If your activities on IRS Schedule E created a loss and your loss is not showing up on line 17 of IRS Form 1040, you may be limited by the Passive Activity Loss limitations. While the Passive Activity Loss limitations demand an entirely separate post on their own, here’s a high level overview:
- If your adjusted gross income (line 37 of IRS Form 1040) is less than $100,000, you are able to take the loss reported on line 26 of Schedule E up to a maximum amount of $25,000 annually.
- If your adjusted gross income is between $100,000 and $150,000, the maximum $25,000 is slowly phased out.
- If your adjusted gross income is over $150,000, you cannot claim the passive loss reported on Schedule E unless you qualify as a real estate professional.
Many investors get worried when they hear this. They’ve been told real estate is a beautiful way to shelter income from taxes but now they are being barred from taking the well deserved losses.
What happens to the losses if you cannot claim them? They are called “unallowed losses” and are reported on IRS Form 8582. This form serves as a catchall that will keep track of all the losses you have not been able to claim over the years.
You do not “lose” these losses; they are simply carried forward until they can offset net rental income. These losses can also be used to offset the gain if you were to sell a rental property, regardless of whether or not the rental property you are selling generated the specific loss.
If the losses get carried forward and you can’t use them, doesn’t that defeat the purpose of sheltering income from taxes?
This is where I have to tell you that you’ve been gurued. Real estate is indeed an excellent way to legally avoid taxation, but for high income earners, you will only be avoiding tax on the rental income, not your regular income from your job.
Again, some amount of income or loss from your rentals should appear on line 17 of your IRS Form 1040. If your adjusted gross income is over $150,000, then you should look for IRS Form 8582 and see if the rental loss has been carried over to it.
Determining Property Basis and Depreciation
One of the most important parts about preparing IRS Schedule E is making sure that we are accurately calculating the rental property cost basis.The most common advice is that the rental property basis is the purchase price plus improvements. So if you buy a property for $100,000 and add $10,000 in improvements, the property basis is $110,000.
This advice, while correct, can be misleading. If you are unaware that you must allocate a portion of the purchase price to land, you will calculate the wrong depreciable basis and therefore deduct an incorrect amount of depreciation.
It’s important to understand how to determine the value of the land of a purchased property. In most cases, the easiest way to get this value is to pull the property’s tax card from the county assessor’s office. Doing so will provide us with a “land ratio” which we will then apply to the purchase price.
For instance, if the property tax card says that the land is worth $10,000 and the improvements are worth $40,000, then our land ratio is 20% [$10,000/($10,000 + $40,000)]. We would then apply this ratio to the purchase price of the property to determine how much value we allocate to land and how much we allocate to improvements.
Why is this important? Because we can only depreciate the value of improvements since land is non-depreciable. Land is ever lasting and does not deteriorate.

Okay, now that we know we can’t depreciate the land value of the building, let’s figure out how to calculate the property basis.
The first thing that I do when preparing IRS Schedule E is a closing cost analysis. I have developed a calculator that helps me quickly calculate a property’s basis.
Resource: Property Basis and Depreciation Calculator
The Closing Cost and Depreciation Calculator is an excellent tool to use when calculating a rental property’s basis because it analyzes all sorts of closing costs such as title transfer fees, bank fees, loan origination fees, escrow, and seller credits. It then places them into the appropriate buckets which we’ll discuss below, and calculates depreciation and amortization for the first year and on an annual basis.
I recommend using some sort of tool, calculator, or guide to help you with the analysis of your closing costs and depreciation because you are going to be lumping costs into three distinct categories:
- Property basis
- Loan cost basis
- Currently deductible expenses
From the property basis, we’ll subtract out our land value to determine the total value in which we will begin depreciating. This is called the depreciable basis.
Purchase Price + Closing Costs – Land Value = Depreciable Basis
Depreciation will usually be over a period of 27.5 years. If you are investing in commercial property, you’re looking at a 39 year period.
Related: How to Calculate Rental Property Depreciation Expense
There are several depreciation methods and conventions. We will be using the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) for our depreciation purposes.
While it sounds like a mouthful, all you need to know is that when you first place a property into service (i.e. advertise it for rent), you will be granted a half month of depreciation. Then, during the first year, you’ll calculate depreciation on a monthly basis.
So if I buy a property and advertise it for rent on September 29, for the first year I’ll have 3.5 months of depreciation (1/2 September + October + November + December). If my annual depreciation is $1,200, I first divide that value by 12 to get it on a monthly basis, then multiply it by 3.5 to figure my first year of depreciation. In our example, it will be $350.
The second category is the loan cost basis which is the sum of all costs associated with the loan. These can be the origination fee, credit report, bank fees, and appraisal fees if one was required by the lender.
Once we calculate the loan cost basis, we will need to determine our annual amortization. Amortization essentially means the same thing as depreciation, it’s just the depreciation method for “intangible” costs.
You will amortize your loan costs over the life of the loan. So if you have a 15 year loan, your amortization period is 15 years. If you have a 30 year loan, your amortization period is 30 years.
Let’s assume our loan cost basis is calculated to be $3,000 and we have a 30 year loan. Each year, you will write-off amortization expense of $100 ($3,000/30 years).
The first year of amortization is calculated much like depreciation in that you will be granted a half month for the month you place the property into service and then amortize on a monthly basis until the end of the year.
The third category is currently deductible expenses which consist of hazard insurance, property taxes (not transfer taxes), and other miscellaneous expenses. These expenses do not need to be amortized or depreciated (whew!) but are simply deducted in full the first year.
Reporting Rental Property on IRS Schedule E
Finally, what you’ve all been waiting for! Before we begin, click this link to open a copy of IRS Schedule E so that you can follow along.For the do it yourself investors, this section will be your tax preparation bible. For all of my clients and everyone who already has a CPA, use this section to cross check the CPA’s work.
The first section is seemingly the easiest but trips plenty of folks up. First, we have to determine whether or not we made any payments that required a 1099. As a general rule, you must issue a 1099 to contractors whom you’ve paid over $600 for work during the year. But luckily for most of my readers, landlords are excluded from this rule.
So if you are a landlord, the common practice is to tick the “no” box when asked if you made payments that require a 1099.
Next we’ll enter the property address and the type of property (single family, multifamily, etc). Hopefully this doesn’t require much more explanation.
Now we need to determine fair rental days, personal use days, and whether or not we are operating a qualified joint venture.
For fair rental days, put the number of days the property was actually rented and producing income. This is especially important if you have rented the property for 14 days or less as then your rental income won’t need to be reported.
Personal use days must also be inputted and can sometimes be confusing. You will only input personal use days if you have used the entire building for personal purposes, or anyone in your family has used the entire building for personal purposes.
So, if you are house hacking (living in one unit and renting out the others), you will not report any personal use days. Instead, you will just split common expenses (mortgage, insurance, property taxes) between IRS Schedule A and E.

A qualified joint venture most often occurs
when two spouses own a property 50/50 and do not live in a community
property state (Arizona, California, Idaho, Louisiana, Nevada, New
Mexico, Texas, Washington, and Wisconsin).
If the spouses of a jointly owned rental live in a community property
state, there is no need to worry about, or elect, the qualified joint
venture status.When rental property is jointly owned by spouses who are not located in a community property state, we have a problem. The spouses must either report their income and losses on a partnership tax return (complicated!) or elect the qualified joint venture status.
Per the IRS Schedule E instructions: “If you and your spouse each materially participate as the only members of a jointly owned and operated rental real estate business and you file a joint return for the tax year, you can elect to be treated as a qualified joint venture instead of a partnership.”
When you and your spouse jointly own an entity that owns your rental property, it can get complicated fast. That discussion is beyond the scope of this post, but you will need to speak with a CPA to sort everything out.
On to the good stuff.
Next we are going to report the rental income received. This is going to be all gross income received from your tenants throughout the year. Gross rental income should include: rental income, refunds received for utilities, and pro-rated rents when you purchased the property.
Expenses are where the tax avoidance (legally) comes into play. I wrote a quick blurb on what to report per expense item:
Advertising – include all general marketing and advertising costs. These can include the cost to place rent signs in the front yard, to advertise on certain websites or publications, to buy business cards, and to send mailers.
Auto and Travel – include all ordinary and necessary auto (to be discussed later) and travel costs required to maintain your rentals. This should not include auto and travel costs incurred to purchase your first rental or to expand your rental business into a new geographic location. Also include 50% travel meals.
Cleaning and Maintenance – include all cleaning expenses to prepare a unit for a tenant or once a tenant moves out. Include maid expenses here as applicable. You should also include maintenance expenses such as painting, mowing, and small upkeep costs of the building, appliances, and equipment.
Commissions – include realtor or property management commissions paid to find a tenant for your unit.
Insurance – include homeowners, hazard, and flood insurance here. Do not pro-rate your annual insurance. You will only report the amount of insurance that you actually pay to your insurance company, not the amount that you pay into escrow.
**A note about escrow – it’s very common to pay insurance and property taxes into escrow on a monthly basis. This protects the lender from your failure to pay these expenses. It’s important to understand that when you pay these expenses into the lender’s escrow account, this is not a deductible expense for you. It is only deductible once the lender actually pays those expenses to the county/city or the insurance agent. That’s when you can deduct the expenses. Why? Paying into escrow is essentially moving money from pocket A to pocket B. It’s still your money and technically an asset on your balance sheet.
Legal and Professional Fees – include expenses related to attorney fees, accounting, and costs of business/financial planning related to your rentals.
Management Fees – include the cost to hire an agent or property manager to manage your rental. This may also include special service calls that the property manager incurs to check on the rental.
Mortgage Interest Paid to Banks – include the amount of interest reported to you by the bank on Form 1098. This amount will be the entire interest the bank has received from you during the year, including the interest you paid during closing.
Other Interest – include the amount of interest paid to third parties, whether they are private investors, private businesses, crowdfunding platforms, or relatives. Also make sure that you have sent these people or parties a Form 1099 showing the interest you have paid them. Without a Form 1099 in this case, you may not be able to substantiate the deduction.
Repairs – include all repairs made to the property that were not considered capital improvements. Expenses here will be small repairs and not the replacement of floors, roofing, etc. You may also include De Minimis Safe Harbor expenses here if they are less than $2,500 and you make the annual election.
Supplies – include the cost of incidental materials and supplies such as paper for printing, small tools, and other small miscellaneous materials that don’t fit into another category.
Taxes – include all tax expenses incurred as a result of owning and operating the rental property. This can include property taxes, school district taxes, and special easements or land taxes. Do not include income taxes.
Utilities – include utility expenses that you have personally incurred, even if the tenant has reimbursed you for them. Do not include utility expenses that the tenant has paid for without you ever having to pay for it. The reason we include utility expenses here even if the tenant has reimbursed you for them is because we are reporting the reimbursement as income at the top of IRS Schedule E and we want to offset that income with the expense you incurred.
Depreciation Expense – include the depreciation expenses that we calculated above with our handy Closing Cost and Depreciation Calculator. Depreciation is an imperative part of IRS Schedule E; don’t mess it up!
Other (list) – include all other expenses incurred while operating the rental but that did not directly fit into any of the categories above. Examples of these expenses may include bank fees, education, HOA fees, subscriptions, cost of books, De Minimis Safe Harbor (if not reported in repairs), meals and entertainment, and gifts to clients or tenants. You will itemize each of your “other” expenses on a separate page.
Once we have all of the expenses inputted into our IRS Schedule E, we add them up and subtract them from our gross rental income. The income or loss for each property will be reported on line 21; if line 21 is a loss, line 22 will show you how much of the loss you can actually deduct.
Line 24 will show you the total net income each property has produced if each property showed net income. If the property instead showed a loss, and you are able to take that loss, you will see the amount on line 25.
Remember, your losses may be limited due to the Passive Activity Loss rules. All of that information will be reported on Form 8582 so definitely review that form if you are showing rental losses.
Line 26 of IRS Schedule E will show the total income or loss that will be reported on line 17 of our Form 1040. But before we calculate line 26, we need to look at Part 2 of IRS Schedule E to report any partnership or S-Corporation income and losses.
Partnerships and S-Corporations will provide you with an IRS Schedule K-1 at the end of the year. That information will be reported on Part 2 of IRS Schedule E.
Basically, we are reporting the name of the partnership, whether it’s a partnership or an S-Corporation, whether it’s foreign owned, and what the employer identification number (EIN) is.
We will then want to report the passive income and non-passive income received from the partnership or S-Corporation. This information will come directly from IRS Schedule K-1 that the partnership or S-Corporation provides you.
Entities must go through the same type of reporting we are doing here with IRS Schedule E. While they use different forms, they are reporting the same information and then providing that information on a summarized form – IRS Schedule K-1.
If you have not received IRS Schedule K-1 but you have an ownership stake in a partnership or an S-Corporation, you have a couple of options. The easiest thing to do is file an extension and wait to file your returns until you actually receive the IRS Schedule K-1. The other option is to go ahead and file your returns, and then file an amended return once you receive IRS Schedule K-1.
Okay, that wraps up IRS Schedule E for the most part. Whatever appears on line 26 will also appear on line 17 of your Form 1040. Make sure that flow is happening correctly to avoid issues.
Reporting Car Expenses and What You Need to Know
You’ll use IRS Form 4562 (link here) to report your car expenses and claim those beautiful IRS deductions.First thing first, if it isn’t documented, you can’t take the deduction. Document everything!
Related: The Real Estate CPA Podcast, Episode #1 – Documentation: The Key to Tax Savings
Next, the question is what should we be documenting? That’s a great question and it depends on your overall strategy.
Many tax advisors recommend using the “actual expense” method in which you record all of your car expenses incurred throughout the year and deduct the portion allocable to the business use. However, it’s important to have a good idea of payoff vs. effort.
Recording and documenting actual car expenses can take a considerable amount of effort. Sometimes, the additional deduction the actual expense method will grant you over the “standard mileage” method simply isn’t worth your time.
I know, you’re probably shocked that a CPA is recommending leaving money on the table. I’m just trying to be realistic.
CPAs want to save you every penny possible without regard to the time it takes you to put all of this information together. They do this because they can show you how much more you saved by working with them and then they can charge you a higher rate.
But if it takes you an additional 10 hours throughout the year to document an additional $500 in deductible business expenses, your tax savings will be your marginal rate multiplied by that $500. So if you’re in the 25% bracket, you’re additional 10 hours of work has saved you $125.
Congratulations, you’ve paid yourself an hourly wage of $12.50.
Now, a $12.50 hourly wage is better than many people, but you are a real estate investor. You have a business to run. Your hourly wage should be over $100.

Related: Tax Write Offs for Car Business Expenses
So what’s my point?
Spend some time estimating your annual deduction using both the standard mileage rate and the actual expense method. Determine, up front, which method will likely yield higher results.
The standard mileage method is great because is very easy to track and takes no time at all thanks to great smart phone apps like MileIQ.
At the end of the year, you’ll compile all of your car expense documentation and report it on page 2, Part V of IRS Form 4562. The total expense will then flow to IRS Schedule E as an Auto Expense.
Putting it All Together
If you stuck with me through that entire article, give yourself a huge pat on the back. You now have the fundamental knowledge required to look at an IRS Schedule E and understand what is going on.We talked about what IRS Schedule E is and how it interacts with the rest of your return. On a high level, we went over what costs go into your rental property cost basis and what you need to do to calculate depreciation (see our Cost Basis and Depreciation Calculator here).
We walked through IRS Schedule E and each expense line item and even talked about car expenses.
If you’re hungry for more or looking for a deeper dive, check out the articles referenced throughout this post. If you want to know more about something, contact us at contact @ therealestatecpa.com and throw in a suggestion for a topic. I’d love to hear from you!
Tuesday, November 28, 2017
1031 exchange
1031 exchange, otherwise known as a tax deferred exchange is a simple
strategy and method for selling one property, that's qualified, and then
proceeding with an acquisition of another property (also qualified)
within a specific time frame. The logistics and process of selling a
property and then buying another property are practically identical to
any standardized sale and buying situation, a "1031 exchange" is unique
because the entire transaction is treated as an exchange and not just as
a simple sale. It is this difference between "exchanging" and not
simply buying and selling which, in the end, allows the taxpayer(s) to
qualify for a deferred gain treatment. So to say it in simple terms,
sales are taxable with the IRS and 1031 exchanges are not. US CODE:
Title 26, §1031. Exchange of Property Held for Productive Use or
Investment
Due to the fact that exchanging, a property, represents an IRS-recognized approach to the deferral of capital gain taxes, it is very important for you to understand the components involved and the actual intent underlying such a tax deferred transaction. It is within the Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code that we can find the appropriate tax code necessary for a successful exchange. We would like to point out that it is within the Like-Kind Exchange Regulations, issued by the US Department of the Treasury, that we find the specific interpretation of the IRS and the generally accepted standards of practice, rules and compliance for completing a successful qualifying transaction. Within this web site we will be identifying these IRS rules, guidelines and requirements of a 1031. It is very important to note that the Regulations are not just simply the law, but a reflection of the interpretation of the (Section 1031) by the IRS.
Due to the fact that exchanging, a property, represents an IRS-recognized approach to the deferral of capital gain taxes, it is very important for you to understand the components involved and the actual intent underlying such a tax deferred transaction. It is within the Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code that we can find the appropriate tax code necessary for a successful exchange. We would like to point out that it is within the Like-Kind Exchange Regulations, issued by the US Department of the Treasury, that we find the specific interpretation of the IRS and the generally accepted standards of practice, rules and compliance for completing a successful qualifying transaction. Within this web site we will be identifying these IRS rules, guidelines and requirements of a 1031. It is very important to note that the Regulations are not just simply the law, but a reflection of the interpretation of the (Section 1031) by the IRS.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)

